Read the article with FishingTheSpot: the lane snapper
Keep an eye on this subject!
Thousands of species spotlights and techniques but also all the local information about your city!


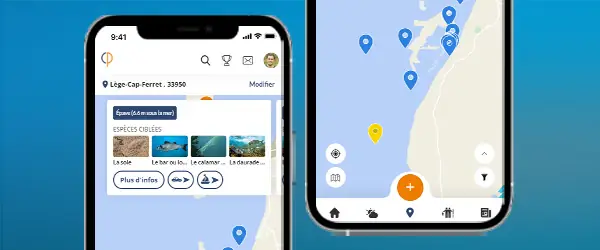
Meet other anglers near you and share your fishing fishing trips, afoot or on a boat, at sea or in freshwater
See the fishing tripsThe Lane Snapper

late spring to early summer
20 cm
Did you fish
this species this month?
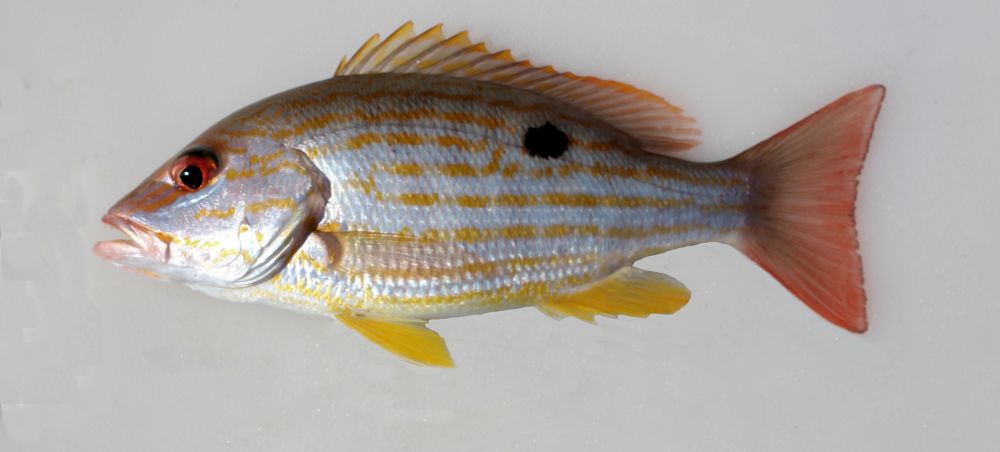
The Lane Snapper belongs to the Lutjanidae family. Lane snappers have an average length of 36 cm and a maximum length of 50 cm. Sexual maturity is achieved at lengths of 10 to 23 cm. The maximum estimated age of the snapper is 10 years. Their spawning period depends on the location. It can be fished in late spring and early summer.
The snapper has a deep body and a pointed snout. It has a double dorsal fin, with a curved anal fin and short pectoral fins. The caudal fin is emarginated to slightly forked. Lane snapper has two color phases. The coloring of the deep water phase is darker and more pronounced than that of the resting phase in shallow water. The two color phases have the upper sides and the backs pink to red with a green shade. The lower sides and belly are silvered with a yellow shade. The head has 3 or 4 yellow bands from the snout to the eye, the lower jaw slightly protrudes. There are eight to ten horizontal yellow to pink stripes on their sides and three or four stripes below their anterior dorsal radius. There is a diffuse black spot under the soft part of the dorsal fin. All fins range from yellow to red.
The Lane snapper lifestyle
Since the snapper living in the corridors lives in a wide range of habitats, they are opportunistic predators feeding on a variety of prey. Snappers feed at night on smaller fish, shrimp, cephalopods, gastropods and crabs.
Spawning occurs in spring and summer, depending on the location. In Cuba, spawning occurs from March to September, with a maximum activity in July and August, while in Puerto Rico, spawning occurs in May. Snappers congregate off the coast during these spawning grounds. Pelagic eggs are discharged into open waters and transported by ocean currents. Once released and fertilized, the eggs hatch within 23 hours. Although the larvae are not well known, they are planktonic at lengths of less than 10 mm. They eventually settle in suitable habitat that provides some protection from predators.
The Lane Snapper habitat
Adult lane snappers live in a variety of habitats, but are most often found on vegetated reefs and sandy bottoms in shallow and shallow waters. This species has also been reported in offshore waters to a depth of 400 meters. Once established, adult snappers remain in the same area throughout their lives. Snappers are also present in seagrass beds associated with shrimp areas. Juveniles live in protected coastal areas.
The snapper is found in the western Atlantic Ocean, from North Carolina to southern Brazil. It is most abundant in the Caribbean, off Panama and on the northern coast of South America. He also performs in Bermuda and the Gulf of Mexico.
The Lane Snapper angling
They are caught with beach seines, boat seines, traps, hand lines and bottom trawls.